Recycling Of Plastic Waste Is One Activity Where Haste Augurs Well
Plastic recycling will reduce reliance on landfills and combats pollution that harms the environment
Recycling Of Plastic Waste Is One Activity Where Haste Augurs Well
With rising concerns about environmental degradation and the harmful effects of plastic waste on ecosystems, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable waste management practices, including recycling
In an effort to build a circular plastics economy in India, a consortium of Indian and Australian research organisations has developed a roadmap to 2035, including a comprehensive view of the entire plastics value chain and systemic policy recommendations.
The team set a goal of recycling 67 per cent of plastic waste by 2035, with an annual consumption of 52.9 million tonnes. To achieve this and other circular economy targets, seven types of policies will be needed: supportive infrastructure, effective recycling, consistent compliance, sustainable consumption, awareness and readiness, design for circularity, and commercial viability.
By 2030, recycling capacity should grow to 18.8 million tonnes and digitalisation of the flow chain of polymers should be mandatory. This year, recycling capacity should hit 35.2 million tonnes and digital product certification and traceability from cradle to grave should be in place. At this point, landfilled plastics should be reduced by 30 per cent and single-use plastics phased out completely.
India Plastic Recycling Market was valued at $4,090.8 million in 2024 and is expected to reach $6,933.2 million by 2033, at a CAGR of 5.22 per cent during the forecast period 2024-2033.
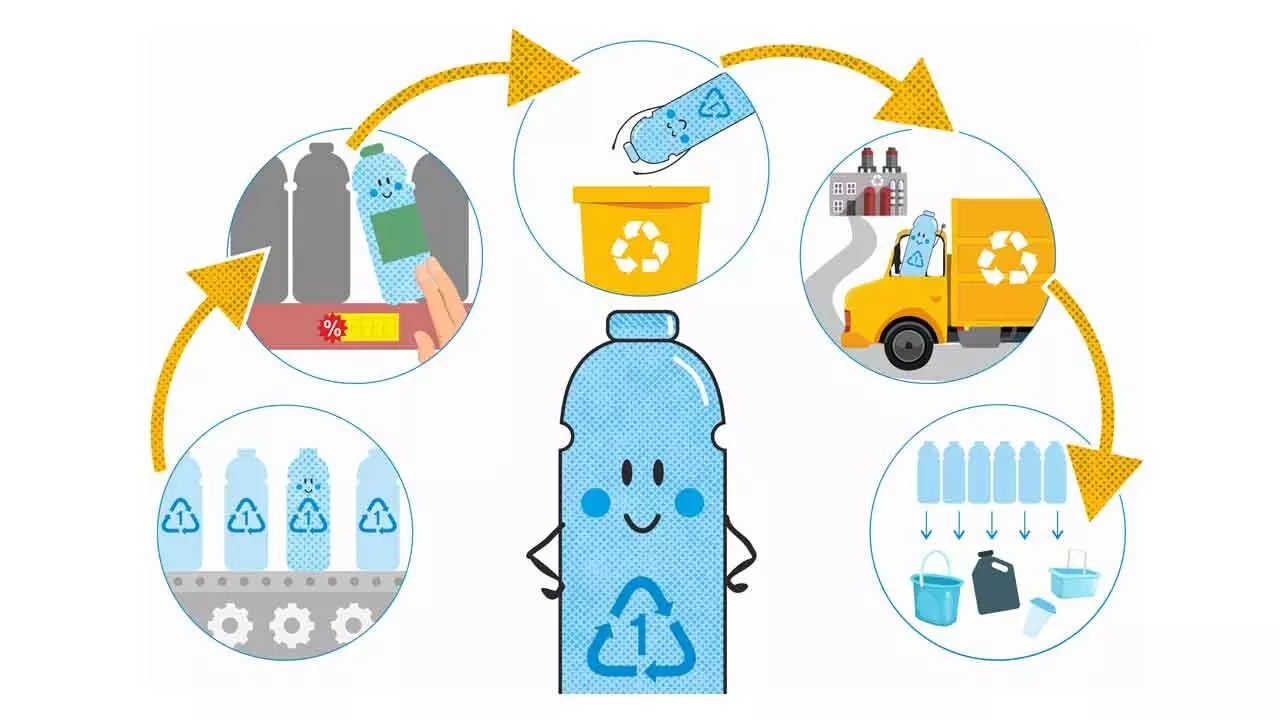
Plastic recycling is the process of giving new life to used plastic items by turning them into usable materials again. It helps reduce our reliance on landfills and combats plastic pollution that harms the environment. There are two main methods: mechanical and chemical recycling.
Mechanical recycling, the most common method, sorts, shreds, washes, and melts down plastic into pellets, which can be moulded into new products like fleece jackets or plastic lumber.
Chemical recycling breaks down plastic on a molecular level and rebuilds it into usable materials or even new plastic.
While plastic recycling offers environmental benefits, it is important to remember that not all plastics are equal. Some plastics are easier to recycle than others, and some may only be recycled a few times before they degrade too much. So, while recycling is important, it’s part of a bigger solution that also involves reducing our overall plastic consumption.
Regulations are in place to impose responsibilities on manufacturers, retailers and consumers to minimise plastic waste generation and promote recycling. For instance, under these rules, plastic waste management has become mandatory for all municipal authorities. As a result, there has been a notable increase in the adoption of plastic recycling practices across various industries and regions in India.
Increasing awareness regarding the environmental impacts of plastic pollution is another significant driver for the plastic recycling market in India. With rising concerns about environmental degradation and the harmful effects of plastic waste on ecosystems, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainable waste management practices, including recycling.
This heightened environmental consciousness has led to a surge in demand for recycled plastic materials across various industries, including packaging, construction, and automotive. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) reported that India generated approximately 9.46 million metric tonnes of plastic waste in 2019-2020, highlighting the urgent need for recycling initiatives to mitigate environmental pollution.
One of the primary challenges hindering the growth of the plastic recycling market in India is the inadequate infrastructure and technology for efficient collection, segregation, and processing of plastic waste. Despite the implementation of regulations promoting recycling, there is a significant gap in the infrastructure required to support large-scale recycling operations.
Many regions lack proper waste collection systems and existing facilities often suffer from obsolete technology and insufficient capacity, which are leading inefficient recycling processes, lower-quality recycled materials, and increased operational costs for recycling businesses.
According to CPCB, only about 60 per cent of plastic waste is collected for recycling in India, highlighting the need for substantial investments in infrastructure development to improve waste management practices.
Another key restraint facing the recycling market is the complexity and inefficiency of plastic waste segregation processes. Effective segregation of the waste is crucial for ensuring high-quality recycled materials and maximizing resource recovery.
However, the current waste management infrastructure in the country lacks proper segregation mechanisms, leading to contamination of recyclable materials and reduced recycling efficiency. Manual segregation processes are labour-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to errors, resulting in lower recycling rates and increased processing costs.
Additionally, the lack of awareness and participation among consumers further exacerbates the challenges associated with plastic waste segregation. The Centre estimates that only about 14 per cent of plastic waste is segregated at source, indicating the urgent need for conducting awareness campaigns to promote proper waste segregation practices among the population.
India's plastics recycling market is expected to evolve significantly due to several factors this year. They include enhancing of investment. The sector has attracted substantial investments—over ₹10,000 crores in recent years—driven by progressive government policies that encourage recycling initiatives and sustainable practices.

