Incentives key to seed and promote CCUS sector in India
Finally India has a clear cut policy framework, a road map to decarbonise by half carbon dioxide emission from the hard-to-abate sectors by 2050
image for illustrative purpose
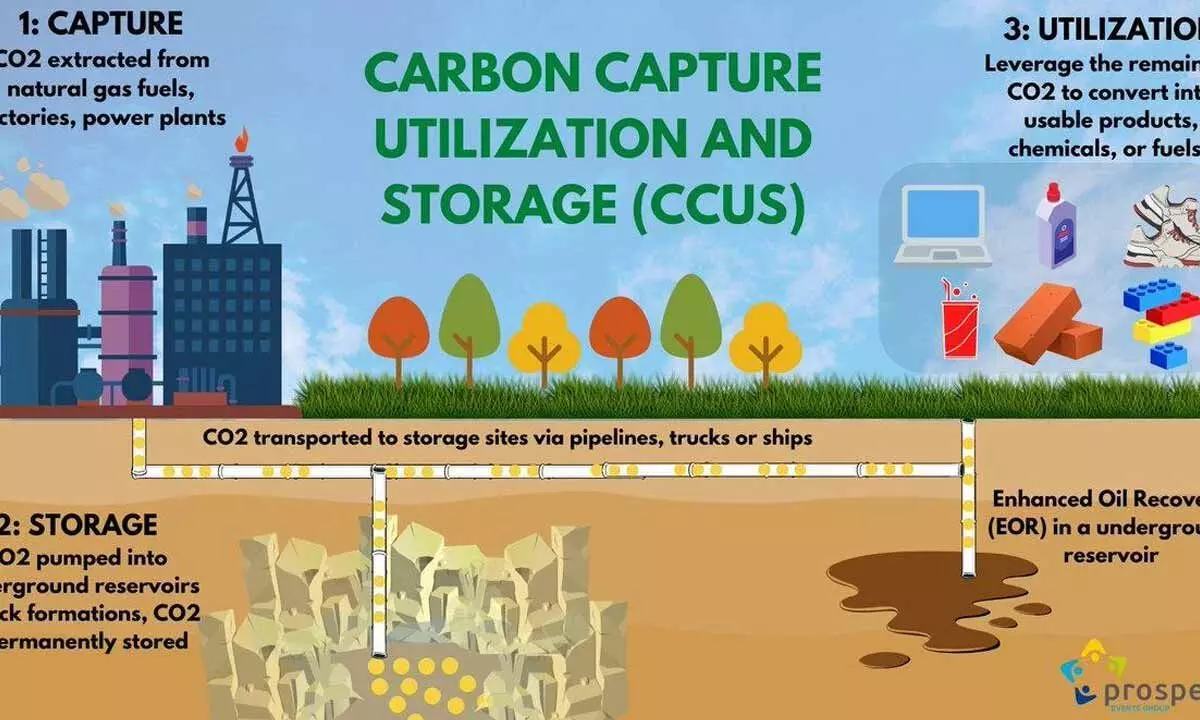
Finally India has a clear cut policy framework, a road map to decarbonise by half carbon dioxide emission from the hard-to-abate sectors by 2050. As reported first by Bizz Buzz, NITI Aayog has now come up with its policy framework: "Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) Policy Framework and its Deployment Mechanism in India" on November 29. The report was actually jointly prepared by NITI Aayog and MN Dastur & Company and after series of parleys and suggestions and feedback from the Union Ministry of Power, Union Ministry of Coal, Union Ministry of Environment, Union Ministry of Steel, Department of Science and Technology, NTPC, ONGC, SAIL, GAIL, BHEL, IOC, Dastur, Tata Steel and other stakeholders.
NITI Aayog top brass was understandably upbeat as CCUS is expected to play an important role in enabling sunrise sectors such as coal gasification and the nascent hydrogen economy in India. This will reduce imports and lead to an Atmanirbhar Indian economy. The key challenge would be to reduce the cost of the mechanisms to implement the technology. NITI Aayog will of course try to develop a consensus with other ministries on the matter.
There is no doubt whatsoever that the focus should be on research and development, particularly in cutting edge technologies. It may be mentioned here that NTPC has already taken up some R&D projects in this regard supported by the Union Power Ministry.
Through proper and effective use of the technology, CO2 emitted from thermal power plants and industries would be captured. This will be particularly well used in high polluting sectors such as steel, cement, oil, gas, petrochemicals, chemicals and fertilisers. Using CCUS technology, the key players in these sectors will be able to make some valorisation of the CO2. There will be an impact on the economy if we are able to get value-added products such as green methanol, green ammonia. They can be produced from this captured CO2 that can be stored on Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage (CCUS).
Going by the report, CCUS can provide a wide variety of opportunities to convert the captured CO2 to different value-added products like green urea, food and beverage form application, building materials (concrete and aggregates), chemicals (methanol and ethanol), polymers (including bio-plastics) and enhanced oil recovery (EOR) with wide market opportunities in India, thus contributing substantially to a circular economy. CCUS projects will also lead to a significant employment generation. It estimates that about 750 mtpa of carbon capture by 2050 can create employment opportunities of about 8-10 million on full time equivalent (FTE) basis in a phased manner.
Having said all these, one has to keep in mind that the private sector is unlikely to invest in CCUS unless there are sufficient incentives or they can be benefitted sufficiently by selling CO2 or gains credits for emissions. Incentives through carbon credits are crucial to seed and promote the CCUS sector in India through tax and cash credits. The successful CCUS implementation in India will be through enactment of a policy framework that supported the creation of sustainable and viable markets for CCUS projects.

