Understanding Tardigrades' Resistance to High Radiation Levels and Its Implications for Future Space Missions
Explore how tardigrades withstand high levels of radiation and discover the implications of their unique resilience for future space missions.
Tardigrade
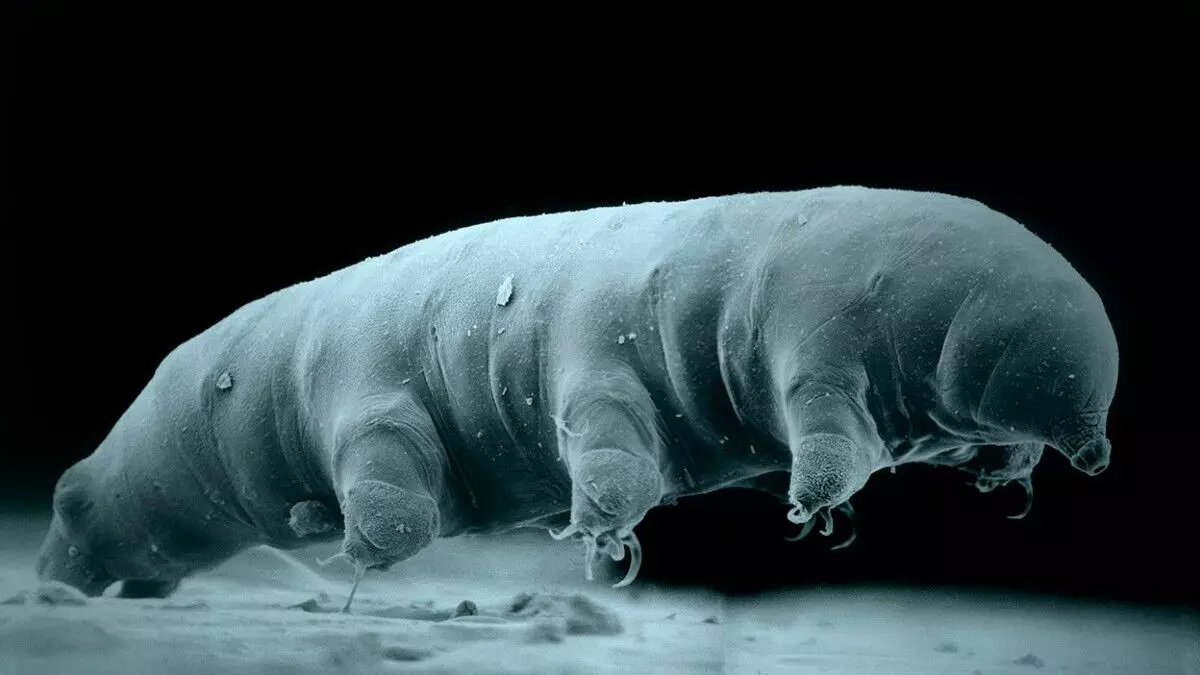
A team of researchers has sequenced the genome of a newly identified species of tardigrade, Hypsibius henanensis, unveiling how these resilient "water bears" can endure extreme radiation. Known for their remarkable ability to survive in hostile environments, tardigrades can withstand radiation levels up to 1,000 times higher than lethal doses for humans. Despite the existence of nearly 1,500 tardigrade species, only a few have been studied extensively.
To delve deeper into this resilience, scientists from multiple institutions in China sequenced the genome of this new species, identifying molecular mechanisms responsible for its extraordinary tolerance. The findings, published in Science, reveal thousands of genes that become active upon radiation exposure, protecting DNA from damage and enabling the repair of any breaks.
The researchers believe that insights from this study could one day help shield astronauts from radiation on space missions, aid in nuclear cleanup, and advance cancer treatments. “This discovery may help enhance stress tolerance in human cells, benefiting patients undergoing radiation therapy,” said co-author Lingqiang Zhang, a molecular biologist at the Beijing Institute of Lifeomics.
Discovered by Zhang’s team in moss samples from Funiu Mountain in China’s Henan province, Hypsibius henanensis was later found to possess 14,701 genes, 30% of which are unique to tardigrades. Exposing the species to 200 and 2,000 grays of radiation, researchers observed 2,801 genes involved in DNA repair, cell division, and immune response.
The study highlights three main factors aiding its radiation resistance: efficient DNA repair mechanisms, the activation of genes producing mitochondria-related proteins that aid in DNA repair, and the generation of antioxidant proteins to minimise cellular damage. Additionally, horizontal gene transfer contributes to the species’ resilience, with 0.5 to 3.1% of its genes acquired from other organisms.

