How aircraft land in dense fog: Navigating zero visibility with technology and skill
image for illustrative purpose
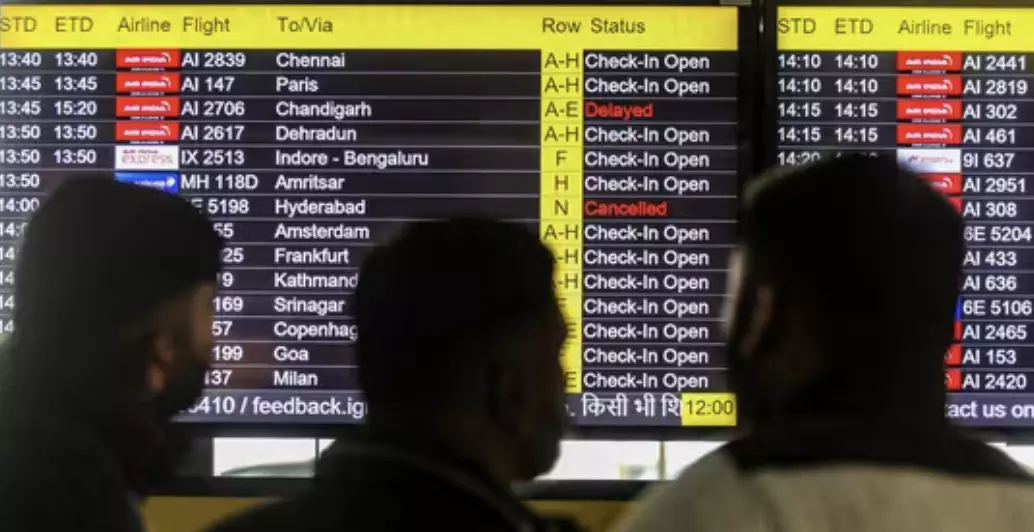
Dense fog continues to disrupt life in Delhi and nearby areas, impacting road, rail, and air travel. On Saturday, low visibility caused by fog led to the diversion of 19 flights and delays for over 200 flights at Delhi's Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGI). This marked the second consecutive day of severe flight disruptions, with Friday witnessing over 400 delays.
How Do Aircraft Land During Zero Visibility?
Aircraft rely on the Instrument Landing System (ILS), a ground-based navigation aid certified by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). This precision system provides pilots with directional (lateral) and descent (vertical) guidance, allowing safe landings even in adverse weather conditions.
Key Components of the Instrument Landing System:
Localiser:
Positioned on the runway's centerline at the opposite end of the approach, this component provides lateral guidance, helping the pilot align the aircraft precisely.
Glide Path:
Offers vertical guidance to maintain the correct descent angle, ensuring a safe approach to the runway.
Distance Measuring Equipment (DME):
Measures the slant distance between the aircraft and the touchdown point on the runway.
Runway Lighting and Visual Aids:
Equipped to assist pilots visually once they approach the decision height or missed approach point (MAP).
Additional Technologies and Support:
Radar Instruments:
Used alongside ILS to monitor the aircraft's descent and ensure it follows the designated path.
Warning Systems:
Alert pilots when the aircraft is off the centerline or deviating from the correct approach.
These systems work seamlessly with the pilot's training and decision-making skills to ensure safe landings. However, the infrastructure at the airport is equally critical.
CAT III Certification: A Key Factor
Airports equipped with Category III (CAT III) ILS can support operations in visibility as low as 50 meters. IGI Airport, with its four CAT III-compliant runways, is among the few globally capable of handling such extreme conditions.
While technology provides significant support, the expertise and experience of pilots remain vital for navigating challenging scenarios like dense fog.

